Going multilingual can multiply organic reach, yet a shaky HubSpot setup can quietly sink rankings. You do not need a new CMS. You need the right URL architecture, clean hreflang and canonicals, a crawlable language switcher, and a workflow that keeps every locale in sync.
This guide is practical and technical without the fluff. We will configure Settings > Website > Languages, create blog variants, localize slugs and metadata, validate sitemaps and redirect maps, use HubDB and CMS GraphQL for data-driven pages, and measure performance by language in GSC, GA, and HubSpot.
Why Go Multilingual on HubSpot
Business case: markets, intent, ROI
Score before you build. Create a one-page model and kill low-ROI locales early.
Demand and intent
-
Build a per-locale keyword set with search volume and intent tags.
-
Map pages to intent buckets: informational, commercial, transactional.
-
Identify local competitors already ranking and the content depth they use.
Back-of-the-envelope forecast
-
Traffic = monthly volume × expected CTR by rank
-
Leads = traffic × localized conversion rate
-
Revenue = leads × win rate × average revenue per account
-
CAC per locale = content cost + translation or transcreation + QA + link building, all divided by new customers
-
Greenlight when payback fits one to three quarters
Operational readiness
-
Decide translation vs transcreation and create a glossary and style guide.
-
Define SLAs for updating all locales when the source changes.
-
Align legal and privacy for forms, emails, and data storage.
What breaks SEO: duplicates, wrong canonicals, missing hreflang
Duplicates
-
Symptom: English and local pages compete for the same query.
-
Causes: reused English slug, no alternates, cross-locale internal links.
-
Fix: create proper language variants, localize slugs, link alternates, keep internal links within the same locale first.
Wrong canonicals
-
Symptom: Google indexes only the English URL.
-
Cause: translated page canonical points to English.
-
Fix: each variant uses a self-referencing canonical.
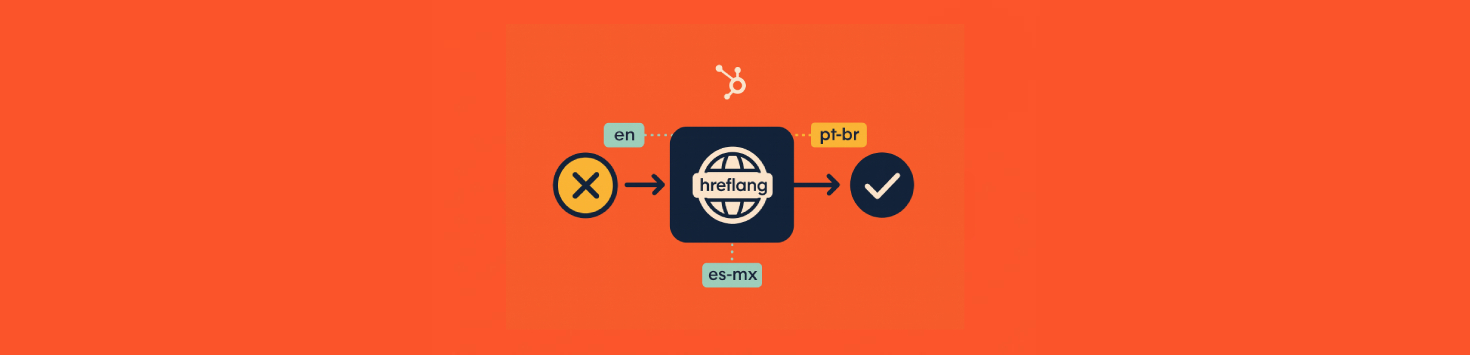
Missing hreflang
-
Symptom: wrong language appears in SERP.
-
Cause: variants not paired or codes are wrong.
-
Fix: create multi-language variations so HubSpot outputs alternates, use correct codes such as pt-br, es-mx, en-gb, and add x-default for the homepage family when applicable.
URL and Language Setup
URL strategy: subdirectories vs subdomains vs ccTLDs
Subdirectories
Pattern: example.com/pt-br/, example.com/es/, example.com/en/
-
Pros: consolidates authority, simple governance, clean reporting.
-
Cons: requires disciplined folder structure.
-
Default choice for most blogs on HubSpot.
Subdomains
Pattern: pt-br.example.com
-
Pros: isolation when stacks differ.
-
Cons: more overhead, dilution risk, more properties to manage.
ccTLDs
Pattern: example.com.br
-
Pros: strongest country signal.
-
Cons: highest cost and fragmentation. Use only with legal or brand requirements.
Conventions
-
Lowercase locale folders with hyphen for region:
/pt-br/and/es-mx/. -
Decide on trailing slash and keep it consistent.
Settings > Website > Languages: primary, variations, locale
Steps you actually perform:
-
Settings > Website > Languages.
-
Set the primary language for each domain or subdomain.
-
Add each target language and select the locale, for example pt-br or es-mx.
-
Confirm date and number formats.
-
Align the URL prefix to your folder plan.
Blog structure: primary blog + language variants
-
Keep one primary blog and create language variants of that blog.
-
Translate posts as multi-language variations so HubSpot emits
hreflangand keeps sitemaps clean. -
Localize title, slug, meta description, image alt text, internal links.
-
Create a subscription email per language when needed.
Navigation and menus per language
-
Use global content for header and footer with a menu per language.
-
All nav links should include the locale path.
-
Add a link-based language switcher in header or footer. Preserve the current path and UTM parameters.
Hreflang and Canonicals
How HubSpot outputs hreflang for blog variants
When you create multi-language variations, HubSpot links alternates automatically. Still validate in source.
Example snippet
<p><link rel="alternate" hreflang="en" href="https://example.com/en/blog/post/" /><br><link rel="alternate" hreflang="pt-br" href="https://example.com/pt-br/blog/post/" /><br><link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-mx" href="https://example.com/es-mx/blog/post/" /></p>
x-default strategy for home and key landing families
-
Add x-default on the canonical homepage or language gateway page if you have several starts.
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/pt-br/blog/post/" /><br>
-
Do not canonical a local page to the English page unless you are consolidating on purpose.
Validation workflow
-
Crawl a sample per locale and check for alternates and self canonical.
-
Use Search Console to confirm coverage and the selected canonical.
-
Fix any missing pairs or incorrect codes.
Localized URLs and Metadata That Rank
Slugs per language
-
Use readable keywords in the local language.
-
Keep slugs short and consistent with the title.
-
Avoid copying the English slug to other locales.
Titles and meta descriptions
-
Match local intent and SERP patterns.
-
Include the locale’s primary keyword near the start of the title.
-
Write unique metas that promise the specific value of the local page.
Open Graph and Twitter Cards
-
Localize OG title and description for better previews and CTR.
Language Switcher UX, Structure, and Performance
Language switcher with crawlable links
-
Do not auto-redirect by browser language.
-
Provide anchor links to each variant and keep UTM intact.
-
Place in header and footer for users and crawlers.
Example HTML
<nav aria-label="Language switcher"><br> <a href="/en/blog/post/?utm_source=newsletter">EN</a><br> <a href="/pt-br/blog/post/?utm_source=newsletter">PT-BR</a><br> <a href="/es-mx/blog/post/?utm_source=newsletter">ES-MX</a><br></nav>
Internal linking and topic clusters per locale
-
Mirror pillar and cluster structure in each language.
-
Link within the same locale first to avoid cross-language cannibalization.
-
Localize breadcrumbs and related posts.
Sitemaps, Article schema, and Core Web Vitals
-
Confirm localized posts appear in the auto sitemap for each host or path.
-
Add
inLanguageinArticlestructured data when applicable.
{<br> "@context": "https://schema.org",<br> "@type": "Article",<br> "inLanguage": "pt-BR",<br> "headline": "Blog Multilíngue no HubSpot",<br> "datePublished": "2025-09-09"<br>}
-
Track Core Web Vitals by locale. Optimize images, fonts, caching and third parties for each market.
Launch and Measure
Redirect and consolidation rules for migrations
-
Inventory current URLs per language.
-
Map one-to-one 301s. Avoid chains. Enforce HTTPS and a single host.
-
Return 410 for content retired without replacement.
Bulk CSV example
/blog/post/;/pt-br/blog/post/<br>/blog/old-guide/;/es-mx/blog/guide/<br>/en/blog/post/;/en/blog/new-post/
Validation workflow in Search Console and crawlers
-
Verify properties for each domain or subdirectory you use.
-
Submit sitemaps per host or path.
-
Monitor Index Coverage and the International report for two to four weeks.
-
Fix missing alternates, wrong canonicals, 404s and unexpected 302s.
KPIs by language
-
From Search Console: impressions, clicks, CTR, position per locale.
-
From GA or HubSpot: sessions, conversion rate, revenue or pipeline by locale.
-
From CRM: lead quality and win rate by language.
-
Update the forecast monthly and shift content budget to the winners.
Quick checklists you can copy
Pre-launch
-
Languages added in Settings with correct locales and URL prefixes
-
Subdirectory strategy documented and applied
-
Primary blog with language variants created
-
Slugs, titles, metas, alt text localized
-
Self canonical present on every variant
-
Hreflang pairs correct and complete
-
Language switcher is link based and preserves path and UTM
-
Localized pages present in the sitemap
-
Redirect CSV prepared and tested in staging
Go-live
-
Upload 301s and spot-check for chains
-
Submit sitemaps and verify properties
-
Crawl samples to confirm alternates and canonicals
-
Monitor logs and catch 404s quickly
Post-launch
-
Review Index Coverage and International Targeting for 2 to 4 weeks
-
Patch missing pairs or wrong codes
-
Compare KPIs by language and iterate titles, metas and internal links
Go multilingual on HubSpot the right way: unify authority with subdirectories, ship true language variants with clean hreflang and self-canonicals, use a crawlable language switcher and tight governance, then measure by locale and scale what works—so you grow internationally without sacrificing the rankings you already own.